
BASICS PART. 1
First of all, after the financial crisis, the world central banks decreased the interest rate from 7 or 8% to close to 1 or 2%. Why are interest rates so low today compared to before the financial crisis?
It’s to stimulate the economy when interest rates are low. It’s easier for people to borrow money and to buy an apartment or a more expensive car because they’re paying a very low interest rate. It’s easier as well for companies to find money what they need to invest and finance their growth. . Today we have a big problem with COVID, economics are weakened substantially but the banks and the central banks cannot lower the interest rate anymore, they’re already very low. So, we’re waiting to see what kind of new ideas they can create.
Anyway, day-to-day fiancial exchanges are still around US$10 trillion, so business as usual !
When confronted to the financial system, you have to take into account different criterias : financial markets, financial management, financial environment, and financing companies. This system has no border, and it awards countries that have an open financial structure; rule of law; low corruption; stable government; low risk environment; good infrastructure. One last criteria to keep in mind : markets tend to overreact !
You should master as well the elementary tools ont the financial market :
– Investment budget: or Capital budgeting,
– Income statement: one of the three important financial statements used for reporting a company’s financial performance over a specific accounting period.
– Balance sheet: financial statement that provides a snapshot of what a company owns and owes, as well as the amount invested by shareholders.
– Cash flow: net amount of cash and cash-equivalents being transferred into and out of a business, meaning that a company can create positive value for shareholders.
The income statement is primarily focused on the company’s revenue and expenses:
Net income = (total revenue + gains) – (total expenses + losses)
An income statement provides valuable insights into a company’s operations, the efficiency of its management, under-performing sectors, and its performance relatives or peers.
It starts with the details of sales and then works down to compute the net income and then the EPS, the EARNINGS PER SHARE! It gives an account on how the net revenue realized by the company gets transformed into net earnings (profit or loss); Based on income statements, management can make decisions like expanding geographically, pushing sales, increase production capacity, or shunting down departments.
SALES
COST OF SALES
GROSS MARGIN
MARKETING
R&D
SELLING & GAL ADMINISTRATION
EBITDA
DEPRECIATION
EBIT
INTEREST
EBT
TAXES
NET INCOME
Fixed costs : not linked to the sales
Variable costs : percentage which varies with sales, linked to sales
Then, you have to be able to read informations about company shares:
Company shares are categorized as follow:
BLUE CHIP: these are mature well-run profitable companies.
HIGH GROWTH: usually young companies that are growing their EPS quickly (or expected to become very profitable in the future)
HIGH INCOME: companies that pay high dividends (EDF, VEOLIA, etc.)
DEFENSIVE: these are companies providing basic needs to people
PENNY: companies with share price below $5, €5 or £5
CYCLICAL: companies whose share price vary with the economy, for example goods or vehicles
SPECULATIVE: high risk companies. There is a chance that investors will lose a lot or all of their money
You heard that it’s a BEAR market for now, What’s the meaning of it?
A BEAR market: a market which is sElling
A BULL market: a market which is bUying
EARNING PER SHARE – EPS
It is calculated as a company profits divided by the number of shares. It serves as an indicator of a company profitability. The higher the EPS is, the more profitable the company is considered:
Company net profit———————————
number of common shares
EPS indicates how much money a company makes for each share of its stock, and is used as a metric for corporate profits. A higher EPS indicates more value because investors will pay more for a company with higher profit. It’s one of the more important variables in determining the share’s price. Example:
EPS is a good indicator to pick stocks. The diluted EPS assumes that all shares have been issued (e.g.: stock options)
It’s a major component to calculate the “price to earning-ratio » (PER)
By dividing a company share’s price by its earning per share, an investor can see the value of the stock in terms of how much the market is willing to pay for each dollar of earning.
PRICE TO EARNING RATIO
It’s the ratio of a company share price to the company earning per share.
Share price
——————
earnings per share
The ration is of a stock (share price) to a flow (EPS). It can be interpreted as the amount of time aver which a company would need to sustain current earnings in order to make enough money to pay back the current share price. The PER is used to determine whether shares are correctly valued in relation to another.
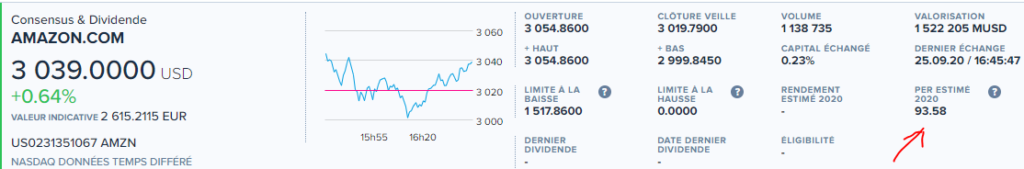
Amazon PER is 93.58. Amazon needs to make profits for 93.58 years in order to pay back its share.
Now let’s have a look at the BONDS market
A corporate bond is a type of debt security that is issued by a firm and sold to investors. The company gets the capital it needs and in return the investor is paid a pre-established number of interest payments at either a fixed or variable interest rate. When the bond expires, or « reaches maturity, » the payments cease and the original investment is returned.
An investor who buys a corporate bond is effectively lending money to the company in return for a series of interest payments, but these bonds may also actively trade on the secondary market.
The highest quality (and safest, lower yielding) bonds are commonly referred to as « Triple-A » bonds, while the least creditworthy are termed « junk ». Fixed rates bonds are 95% of the market. The coupon or interest rate is fixed for the life of the bond.
The PAR, or nominal value of bonds are 1 followed by a minimum of two “zeroes” ($ or €) so:
100
1 000
10 000
100 000
1 000 000
Coupon or interest rate is always paid on the nominal value of the bond. At the end of the life of the bond, it is the Par or nominal value that is repaid, and not the purchase price.
Let’s imagine that you are purchasing a BOND for $1020, life 8 years, coupon 3.2%. How do you calculate the YELD to Maturity ?
First : the CAPITAL GAIN OR LOSS: PAR VALUE-PAID PRICE so $1000 – $1020 = -$20
Then INTEREST INCOME: 8 years x 3.2% on $1000 = $256
and TOTAL INCOME: $256-$20 = $236
AVERAGE ANNUAL INCOME: $236/8 = $29.5
YELD TO MATURITY: $29.5/$1020 = 2.98%
Formula is :
[(CAPITAL GAIN OR LOSS + INTEREST INCOME)/AVERAGE ANNUAL INCOME]/PAID PRICE
or
[((interest rates*PAR Value*duration coupon) + (PAR value-paid price))/duration]/paid price
Different sort of BONDS :
– Fixed rate Bonds –> Bonds with a fixed interest rate
– Floating rate Bonds –> Bonds who interest rate varies with market rate
– Callable Bonds –> Bonds that may be repaid early by the company -> a bond that the issuer may redeem before it reaches the stated maturity date. A callable bond allows the issuing company to pay off their debt early, so the interest rate will be higher to be very attractive to investors.
– Inflation Indexed Bonds –> Bonds whose interest rate is indexed with inflation
– Junk Bonds –> Bonds which have an Agency rating lower than “BB”. Bonds that carry a higher risk of default than most bonds issued by corporations and governments. They are issued by companies that are struggling financially and have a high risk of defaulting or not paying their interest payments or repaying the principal to investors.
– Zero coupon Bonds –> Bonds that pay no interest/coupon. Financial assets on the Monetary interbank markets have no interest rate.
– Convertible Bonds –> Bonds that may be converted into ordinary shares. It may attract investors who beleive in the future of the company and who rather have company’s shares than being repaid by the company. It’s a powerful incentive.

Poster un Commentaire
Vous devez vous connecter pour publier un commentaire.